Drum brakes are a braking system commonly used in cars, trucks, vans, and buses. They consist of a cylindrical drum, which rotates with the wheel, and brake shoes, which press against the inside of the drum to slow the vehicle down. Drum brakes have been used in vehicles for decades and are known for their durability and reliability. They are also relatively easy to maintain and can be serviced by most mechanics.
One of the main benefits of drum brakes is their compact design, which makes them a good option for vehicles with limited space for braking components. They are also relatively inexpensive to manufacture and install, making them a cost-effective option for many vehicles.
What is a Drum Brake and its material?
A drum brake is a type of braking system that uses brake shoes to press against the inner surface of a brake drum to slow or stop a vehicle. The brake shoes are typically made of friction material and are housed within a brake drum, which is typically made of cast iron or aluminum.
When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, a brake master cylinder converts the force into hydraulic pressure, which is then sent through brake lines to the brake drums. Inside the brake drums, brake shoes are pressed against the inner surface of the drums by brake pistons, creating friction that slows or stops the vehicle.
The brake shoes are typically held in place by a brake drum, which is attached to the wheel hub. As the brake shoes press against the drum, the friction between the shoes and the drum causes the wheel to slow down. The brake drum also serves as a heat sink, dissipating the heat generated by the friction between the brake shoes and the drum.
Drum brakes are typically used on the rear wheels of vehicles, as they are cheaper to manufacture and less complex than disc brakes, which are typically used on the front wheels. However, drum brakes are less efficient than disc brakes and can be less effective in stopping a vehicle in wet or slippery conditions.
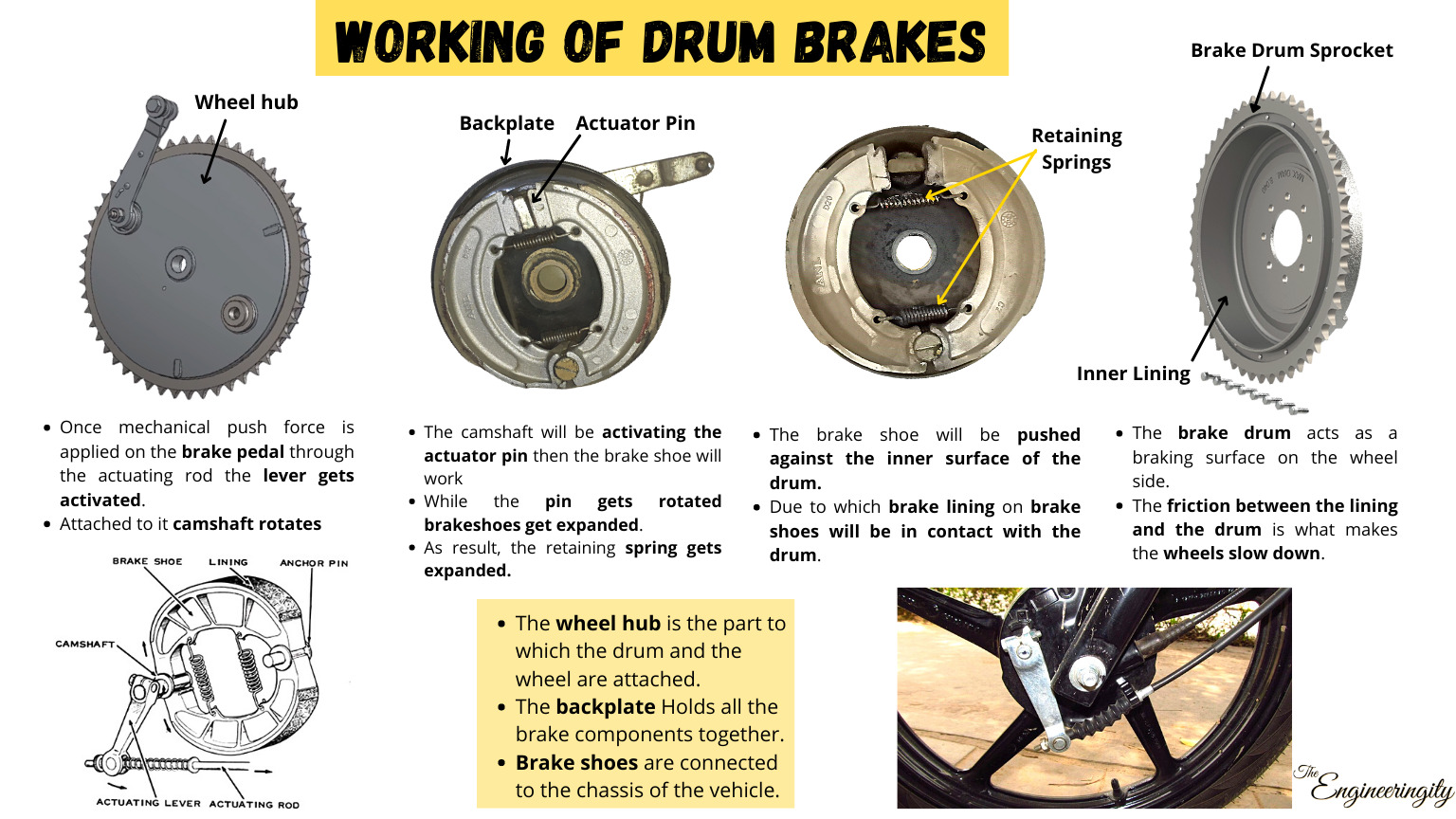
Components of Drum Brakes and their working
Brake shoes: These are the friction pads that press against the brake drum to slow down or stop the vehicle.
Brake drum: This is the cylindrical component that the brake shoes press against to slow down or stop the vehicle.
Wheel cylinder: This is the component that pushes the brake shoes against the brake drum when the brake pedal is pressed.
Return springs: These springs push the brake shoes back to their original position when the brake pedal is released.
Adjusting mechanism: This is used to adjust the distance between the brake shoes and the brake drum.
Hardware: This includes the mounting hardware and fasteners that hold the brake assembly in place.
Functioning of Brake Drum:
When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid is sent through the brake lines to the wheel cylinder. This causes the piston in the wheel cylinder to push the brake shoes against the brake drum. The friction between the brake shoes and the brake drum slows down or stops the vehicle. The return springs push the brake shoes back to their original position when the brake pedal is released. The adjusting mechanism is used to ensure that the brake shoes are the correct distance away from the brake drum.
How to Tell if Your Drum Brakes Need Replacement
Several signs indicate your drum brakes may need replacement. Here are some of the most common indications that your drum brakes need attention:
Reduced braking power: If you notice that your brakes are not working as effectively as they used to, it may be time to replace the drums.
Grinding or squealing noise: If you hear a grinding or squealing noise when you apply the brakes, this could be a sign that the drums are worn and need to be replaced.
Vibration or pulsation: If you feel a vibration or pulsation in the brake pedal when you brake, this could be a sign that the drums are out of round or have excessive wear.
Pulling to one side: If your vehicle pulls to one side when you brake, this could indicate that the drums are unevenly worn and need to be replaced.
Warning light: If your vehicle's brake warning light comes on, it could indicate that there is an issue with the drum brakes.
Scraping or dragging sound: If you hear a scraping or dragging sound when you are driving, it could be a sign that the drums are worn and need to be replaced.
If you notice any of these signs, it is important to have your drum brakes inspected by a professional mechanic as soon as possible. In most cases, drum brakes need to be replaced when they have worn out or have been damaged.
Why Drum Brakes are used?
Drum brakes are used for a variety of reasons, including:
Cost: Drum brakes are generally less expensive to manufacture and install than disc brakes, making them a cost-effective option for many vehicles.
Durability: Drum brakes are known for their durability and can withstand heavy use and harsh conditions.
Space-saving design: Drum brakes are compact in design, making them a good option for vehicles with limited space for braking components.
Easy maintenance: Drum brakes are relatively easy to maintain and can be serviced by most mechanics.
Versatility: Drum brakes can be used in a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, vans, and buses.
Reliability: Drum brakes are known for their reliability and can last for many years with proper maintenance.
Traditional use: Drum brakes have been used in vehicles for decades, and many manufacturers continue to use them in their vehicles as they are a proven technology.
Better heat dissipation: Drum brakes can dissipate heat better than disc brakes, which makes them ideal for vehicles that are driven for long periods or for heavy-duty use.
However, drum brakes can be less efficient than disc brakes in terms of stopping power, especially in wet or muddy conditions. They tend to generate more heat than disc brakes which can lead to brake fade if the vehicle is driven for long periods or for heavy-duty use.
Overall, drum brakes are a proven technology that is widely used in vehicles for their cost-effectiveness, durability, and reliability.